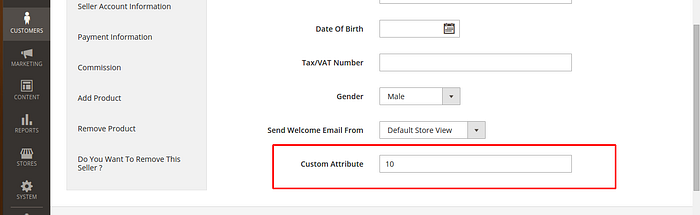
Here we will learn, How to create a Customer Custom attribute in Magento 2.
Note: We also have a separate module (Magento 2 Custom Registration Fields) that allows the admin to create custom fields for customers.
Henceforth, using this module you can extend your customer sign-up form. For more information, you can check it on our store.
Let’s start the process.
We can achieve this by using the following methods:
1st Method: Using InstallData file
Create the file Webkul\CustomAttribute\Setup\InstallData.php
<?php namespace Webkul\CustomAttribute\Setup; use Magento\Customer\Setup\CustomerSetupFactory; use Magento\Customer\Model\Customer; use Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\Set as AttributeSet; use Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\SetFactory as AttributeSetFactory; use Magento\Framework\Setup\InstallDataInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface; class InstallData implements InstallDataInterface { /** * @var CustomerSetupFactory */ protected $customerSetupFactory; /** * @var AttributeSetFactory */ private $attributeSetFactory; /** * @param CustomerSetupFactory $customerSetupFactory * @param AttributeSetFactory $attributeSetFactory */ public function __construct( CustomerSetupFactory $customerSetupFactory, AttributeSetFactory $attributeSetFactory ) { $this->customerSetupFactory = $customerSetupFactory; $this->attributeSetFactory = $attributeSetFactory; } public function install(ModuleDataSetupInterface $setup, ModuleContextInterface $context) { /** @var CustomerSetup $customerSetup */ $customerSetup = $this->customerSetupFactory->create(['setup' => $setup]); $customerEntity = $customerSetup->getEavConfig()->getEntityType('customer'); $attributeSetId = $customerEntity->getDefaultAttributeSetId(); /** @var $attributeSet AttributeSet */ $attributeSet = $this->attributeSetFactory->create(); $attributeGroupId = $attributeSet->getDefaultGroupId($attributeSetId); $customerSetup->addAttribute(Customer::ENTITY, 'custom_cust_attribute', [ 'type' => 'varchar', 'label' => 'Custom Attribute', 'input' => 'text', 'required' => false, 'visible' => true, 'user_defined' => true, 'position' => 999, 'system' => 0, ]); $attribute = $customerSetup->getEavConfig()->getAttribute(Customer::ENTITY, 'custom_cust_attribute') ->addData([ 'attribute_set_id' => $attributeSetId, 'attribute_group_id' => $attributeGroupId, 'used_in_forms' => ['adminhtml_customer'],//you can use other forms also ['adminhtml_customer_address', 'customer_account_edit', 'customer_address_edit', 'customer_register_address', 'customer_account_create'] ]); $attribute->save(); } }InstallData conforms to InstallDataInterface , which requires the implementation of the install method that accepts two parameters of type ModuleDataSetupInterface and ModuleContextInterface .
Using the addAttribute method on the instance of Magento\Customer\Setup\CustomerSetupFactory, we are instructing Magento to add a number of attributes.
Note: The module’s module.xml file must have setup_version to create customer custom attribute using InstallData. To know steps to create module in Magento 2, you can check our another blog here.
2nd Method: Using Data Patch
In this method, we need to create a data patch file as CreateAttributes.php in our custom module Setup folder. Note: You can also use the different file name and class name.
complete path: app/code/Webkul/CustomAttribute/Setup/Patch/Data/CreateAttributes.php
To know more about data and schema patches, click here.
<?php namespace Webkul\CustomAttribute\Setup\Patch\Data; use Magento\Framework\Setup\Patch\DataPatchInterface; use Magento\Customer\Setup\CustomerSetupFactory; use Magento\Customer\Model\Customer; use Magento\Eav\Model\Entity\Attribute\SetFactory as AttributeSetFactory; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface; class CreateAttributes implements DataPatchInterface { /** * @var ModuleDataSetupInterface */ private $moduleDataSetup; /** * @var CustomerSetupFactory */ protected $customerSetupFactory; /** * @var AttributeSetFactory */ private $attributeSetFactory; /** * @param ModuleDataSetupInterface $moduleDataSetup * @param CustomerSetupFactory $customerSetupFactory * @param AttributeSetFactory $attributeSetFactory */ public function __construct( ModuleDataSetupInterface $moduleDataSetup, CustomerSetupFactory $customerSetupFactory, AttributeSetFactory $attributeSetFactory ) { $this->moduleDataSetup = $moduleDataSetup; $this->customerSetupFactory = $customerSetupFactory; $this->attributeSetFactory = $attributeSetFactory; } /** * Add eav attributes */ public function apply() { /** @var CustomerSetup $customerSetup */ $customerSetup = $this->customerSetupFactory->create(['setup' => $this->moduleDataSetup]); $customerEntity = $customerSetup->getEavConfig()->getEntityType('customer'); $attributeSetId = $customerEntity->getDefaultAttributeSetId(); /** @var $attributeSet AttributeSet */ $attributeSet = $this->attributeSetFactory->create(); $attributeGroupId = $attributeSet->getDefaultGroupId($attributeSetId); $customerSetup->addAttribute(Customer::ENTITY, 'custom_customer_attribute', [ 'type' => 'varchar', 'label' => 'Custom Attribute', 'input' => 'text', 'required' => false, 'visible' => true, 'user_defined' => true, 'position' => 999, 'system' => 0, ]); $attribute = $customerSetup->getEavConfig()->getAttribute(Customer::ENTITY, 'custom_customer_attribute') ->addData([ 'attribute_set_id' => $attributeSetId, 'attribute_group_id' => $attributeGroupId, 'used_in_forms' => ['adminhtml_customer'],//you can use other forms also ['adminhtml_customer_address', 'customer_account_edit', 'customer_address_edit', 'customer_register_address', 'customer_account_create'] ]); $attribute->save(); } /** * Get dependencies */ public static function getDependencies() { return []; } /** * Get Aliases */ public function getAliases() { return []; } }After adding these files, run the following command in your magento2 root directory through a terminal.
php bin/magento setup: upgrade
That is all for the How to Create Customer Custom Attribute in Magento 2. Hope it will help you. Thank you.
Originally published at https://webkul.com on February 19, 2016.
Comments
Post a Comment